整場比賽看的題目不多,主要都卡在 Tarmain 的數學式,於是就把這兩題自己有看的題目寫成比較詳細的題解
Reverse1: Reversing iS Amazing
程式碼如下,簡單來說程式中保存了兩段空間,一段存放 private key 一段存放密文,程式執行時會要你輸入明文,經過程式用 private key 加密後如果與密文一致後會印出 correct
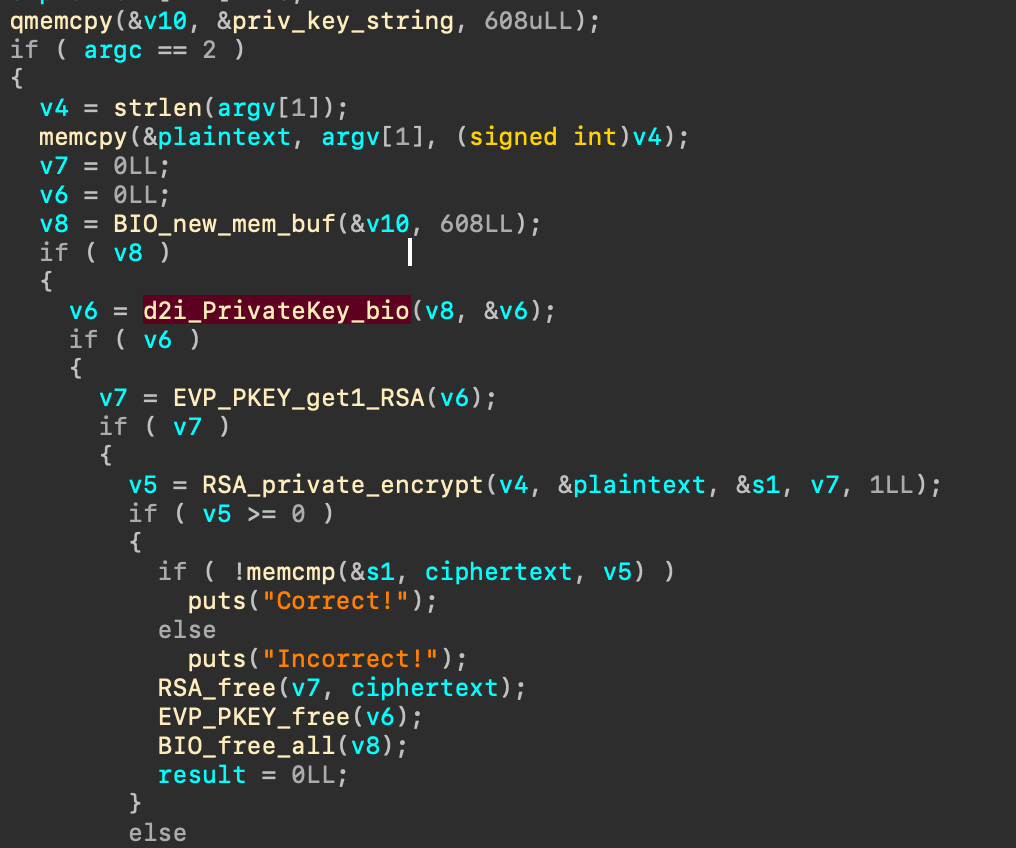
依據自己在使用 RSA 的想法,就算得到 private key 或是 public key 都無法推出另一方,因此下一步就是來翻翻 openssl 的 library 了解一下 openssl API 的用途
openssl library d2i_PrivateKey_bio 解釋 OpenSSL example
重點
- BIO is an I/O stream abstraction
- EVP_PKEY objects are used to store a public key and (optionally) a private key
- d2i_PrivateKey_bio functions return a valid EVP_KEY structure
總結
程式中呼叫完 d2i_PrivateKey_bio 的 return value V7 會帶有 private 和 public key,所以我們只要抓到 EVP_KEY 然後執行 RSA_public_decrypt 將密文轉回明文就成功了
解法
可以將密文和private key 取出,再自己額外寫一個程式來解。但這邊要介紹另一種作法,是我看到別人的 writeup 覺得效率更高,步驟如下
- hooking RSA_private_encrypt
- 在 argument 第四個 拿到 EVP_KEY structure
- Calling RSA_public_decrypt
- 填入剛剛的 EVP_KEY structure 就可以得到明文
frida
frida 是個蠻好用的動態插針(instrucment) 的工具 官方教學文件
frida 使用
大部分 frida 的應用會在 hook 執行的 process,而這次是直接執行一隻程式,所以稍微紀錄一下如何使用 frida
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
pid = frida.spawn(["rsa", "argv1", "argv2"]) # create a suspand process
session = frida.attach(pid)
script = session.create_script("""
<your action>
""")
def on_message(message, data):
print(message)
script.on('message', on_message)# output frida script message
script.load()
frida.resume(pid) # must load script before resume
raw_input() # keep this script running
Function argument
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
int RSA_private_encrypt(
int flen,
unsigned char *from,
unsigned char *to,
RSA *rsa,
int padding);
int RSA_public_decrypt(
int flen,
unsigned char *from,
unsigned char *to,
RSA *rsa,
int padding);
最後程式碼
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
from __future__ import print_function
import frida
import sys
pid = frida.spawn(["rsa", "TWCTF{*****************************}"])
session = frida.attach(pid)
script = session.create_script("""
var rsaKey=null;
Interceptor.attach(Module.findExportByName(null, 'RSA_private_encrypt'), {
onEnter: function (args) {
console.log('input len.:', args[0]);
console.log('input.....:', args[1].readCString());
console.log('output ptr:', args[2]);
console.log('key.......:', args[3]); rsaKey = args[3];
console.log('padding...:', args[4]);
}
});
const RSA_public_decrypt = new NativeFunction(Module.findExportByName(null, 'RSA_public_decrypt'), 'int', ['int', 'pointer', 'pointer', 'pointer', 'int']);
Interceptor.attach(Module.findExportByName(null, 'memcmp'), {
onEnter: function (args) {
var x = Memory.alloc(0x80);
RSA_public_decrypt(0x80, args[1], x, rsaKey, 1);
//dump("Flag", x);
console.log(hexdump(x));
},
});
""")
def on_message(message, data):
print(message)
script.on('message', on_message)
script.load()
frida.resume(pid)
raw_input()
Reverse2: Tamarin
這題解開是個 APK 檔,於是先用 adb 把他裝進 android 手機裡面 (由於這隻 APK 只能跑在 ARM 的架構,還好實驗室手機一堆),從下圖可以發現就是個很簡單的介面,可以輸入 Flag 然後按下button 檢查正確性。
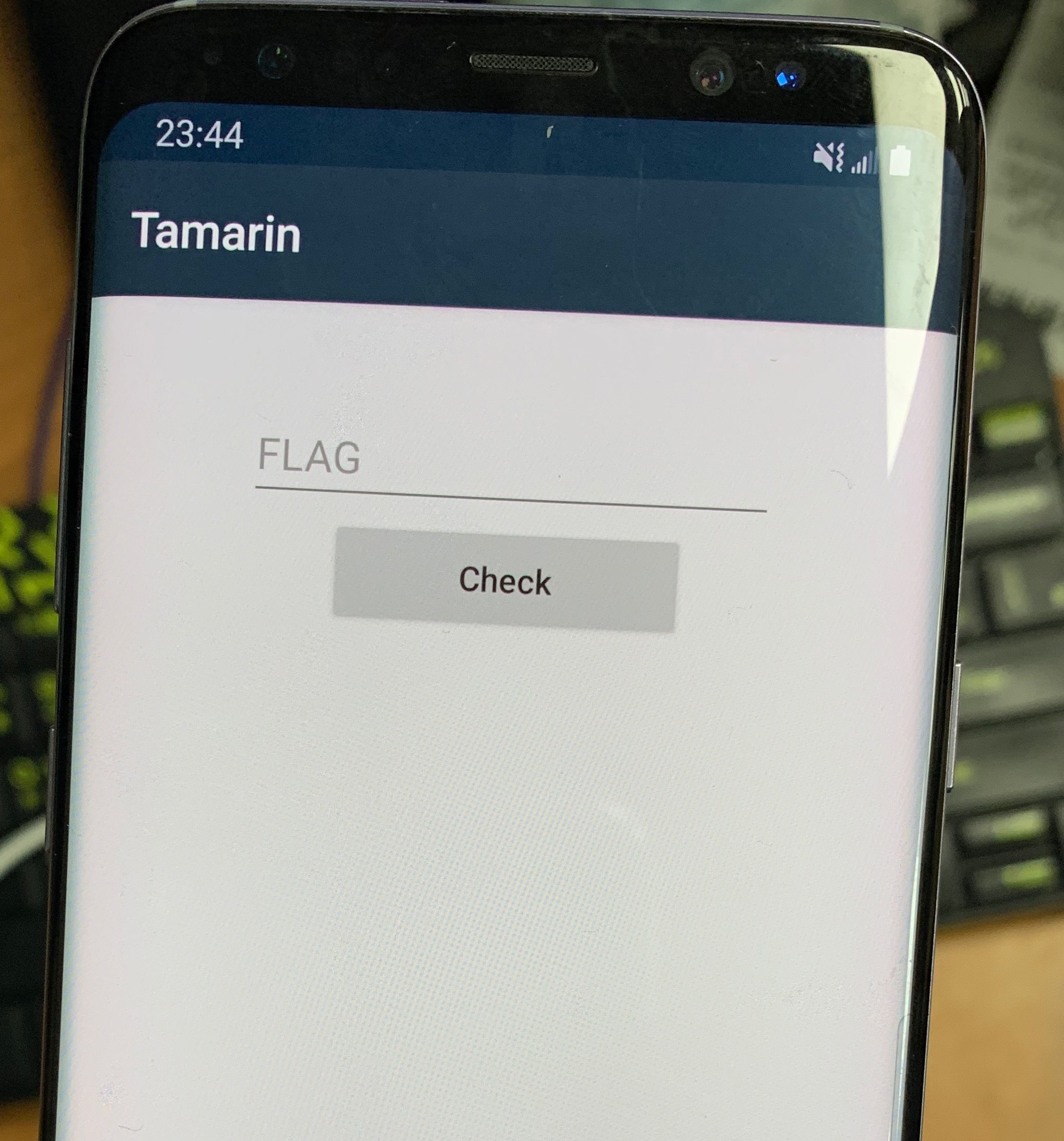
利用 jd-gui 把整個 APK 翻爛後還是沒找到關鍵程式,後來細看引用的 library 才發現這隻 APK 是使用 Mono 的框架,利用 .NET 來寫的,果然我還太菜了,看這麼久才發現。
mono_unbundle
科普了一下 mono 的框架後,就找到可以將 library 轉回 .NET 的工具 mono_unbundle ,果然是前人種樹呀,這工具可以直接把 lib/libmonodroid_bundle_app.so 轉回一包 .NET 程式碼
Tamarin.dll 內容
快速地介紹一下程式碼,輸入的 FLAG 會放進 Check.Func4 做檢查,而Func4 一開始會將 flag 四個四個切,然後分別放入二維陣列 equations_arr[32][22] 的首位。
接著進入檢查環節 程式會 random 一個數值,然後將 equations_arr[-1] 陣列當作係數,random直當作 X,計算 Y,接著再把 Y 當 X 重跑循環 10000 次 最後比對結果與 equations_arr[i] 的最後一個值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
...
EditText flagText = base.FindViewById<EditText>(2131230795);
...
{
if (Check.Func4(flagText.Text))
{
flagText.Text = "The flag is TWCTF{" + flagText.Text + "}";
return;
}
flagText.Text = "Invalid";
};
}
}
public static bool Func4(string flag)
{
...
// put user input into array
for (int j = 0; j < Check.equations_arr.GetLength(0); j++)
{
List<uint> list2 = new List<uint>();
list2.Add(BitConverter.ToUInt32(bytes, j * 4));
for (int k = 0; k < Check.equations_arr.GetLength(1); k++)
{
list2.Add(Check.equations_arr[j, k]);
}
list.Add(list2);
}
Parallel.ForEach<List<uint>>(list, parallelOptions, delegate(List<uint> equation)
{
object lockObj = lockObj;
lock (lockObj)
{
uint num = Check.randFunction();
for (int l = 0; l < 10000; l++)
{
num = Check.countPolynomial(equation, num, equation.Count - 2);
}
checkResults.Add(num == equation[equation.Count - 1]);
}
});
return Enumerable.All<bool>(checkResults.ToArray(), (bool x) => x);
private static readonly uint[,] equations_arr = new uint[,]
{
...
{
...
2921822136U,
1060277104U,
...
},
...
{
...
463101660U,
3469888460U,
...
}
...
}
}
解法 1
解題的重點在於他其實在跑 10000 次的過程會漸漸收斂在同一個數,因此可以利用 Z3 來寫算式,這個算式是隊友想到的,因為在40次後就會收斂利用這點可以讓速度更快一點,其他就交給 Z3 來算
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
def g(x):
for _ in range(40):
x = f(x)
return x
s = Solver()
s.add(g(0) == coeffs[-1])
s.check()
print(s.model()[F].as_long().to_bytes(4, 'little').decode())
解法2
這解法是在別人的blog看到的,想法就是最後一定會變成x=f(x) 並且最後迭代完 f(x) 一定要等於 equations_arr[-1],因此就直接將 equations_arr[-1] 帶入x 就好。
